 C.
C.
Full experimental details for obtaining the data in this paper have
recently been presented (Zhang et al., 1995b). Briefly,
DPPC (1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine)
from Avanti Polar Lipids (Alabaster, AL) was dispersed in pure water or
aqueous PVP (polyvinylpyrrolidone) solutions and sealed in
thin walled glass capillaries. The maximum PVP concentration was
nominally 50% (w/w) which corresponds to 98% relative humidity
(McIntosh and Simon, 1986a). All data were taken from samples at 50 C.
C.
High resolution X-ray scattering experiments were performed at
the Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source (CHESS) on the F3 station.
A double bounce Si monochromator was calibrated to 1.2147Å
X rays, the scattering angles were selected by Bragg diffraction
from the (111) face of a Si analyzer
crystal, and the intensity was measured by a NaI scintillation detector.
The longitudinal resolution had half width at half maximum
of either 1.0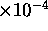 Å
Å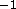 or 3.3
or 3.3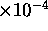 Å
Å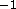 .
The out-of-scattering plane resolution was
.
The out-of-scattering plane resolution was
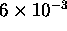 Å
Å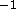 and this caused a small amount of
slit smearing in the first order peak that was, however, easily
accommodated in the theoretical fits to the data.
and this caused a small amount of
slit smearing in the first order peak that was, however, easily
accommodated in the theoretical fits to the data.
Significant radiation damage, as detected by observing changes in peak shapes and positions and by thin layer chromatography, was avoided by systematically exposing different spots on the capillary of the same sample to the x-ray beam (Zhang et al., 1995b). To obtain the relative intensities of different orders measured on different spots, brief scans of the intense first order peak were taken on each spot for normalization. Weak background scattering from capillaries containing air, pure water, 25% PVP solution and 50% PVP solution was measured using long counting times. The angular range of the reported data for the tails of the peaks was restricted so that the average intensity was at least twice as great as the background. Typical data are shown in Fig. 1.